DhcpMonitor
Use this monitor to check the availability and functionality of DHCP servers. The DhcpMonitor is run by Pollerd and opens a background process to listen for incoming DHCP responses. A DHCP server is tested by sending a DISCOVER message. If the DHCP server responds with an OFFER, the service is marked as up. The background listening process is started only if the DhcpMonitor is used.
Make sure no DHCP client is running on the Meridian server and using port UDP/67 and UDP/68.
If UDP/67 and UDP/68 are already in use, you will find warning messages in your log files.
You can test if a process is listening on UDP/68 with sudo ss -lnpu sport = :68.
|
| The use of the DhcpMonitor previously required the installation of an additional package. The functionality of this additional plugin has been rolled into the core Meridian service and is no longer a separate install. |
Monitor facts
Class Name |
|
This monitor implements the Common Configuration Parameters.
DhcpMonitor configuration
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
macAddress |
The MAC address that Meridian uses for a DHCP request. |
00:06:0D:BE:9C:B2 |
relayMode |
Puts the poller in relay mode. |
false |
myIpAddress |
This parameter will usually be set to the IP address of the Meridian server, if relayMode is set to true. In relay mode, the DHCP server being polled will unicast its responses directly back to the IP address specified by myIpAddress rather than broadcasting its responses. This lets DHCP servers be polled even though they are not on the same subnet as the Meridian server, and without the aid of an external relay. |
127.0.0.1 |
extendedMode |
When extendedMode is false, the DHCP poller sends a DISCOVER and expects an OFFER in return. When extendedMode is true, the DHCP poller first sends a DISCOVER. If it receives no valid response it sends an INFORM. If that returns no valid response, it sends a REQUEST. OFFER, ACK, and NAK are all considered valid responses in extendedMode. |
false |
requestIpAddress |
This parameter applies only to REQUEST queries sent to the DHCP server when extendedMode is true. The query requests the specified IP address. |
127.0.0.1 |
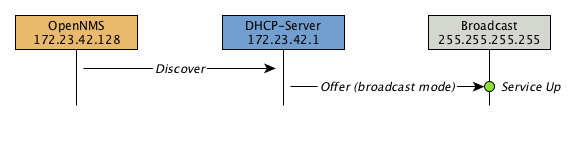
Example: testing DHCP server in the same subnet
Example configuration on how to configure the monitor in poller-configuration.xml.
The monitor tries to send a maximum of three DISCOVER messages and waits three seconds for the DHCP server OFFER message.
Examples use CentOS/RHEL path name.
For Debian/Ubuntu, use /var/lib/opennms/rrd/response.
poller-configuration.xml<service name="DHCP" interval="300000" user-defined="false" status="on">
<parameter key="retry" value="2" /> (1)
<parameter key="timeout" value="3000" /> (2)
<parameter key="relayMode" value="false"/> (3)
<parameter key="extendedMode" value="false"/> (4)
<parameter key="rrd-repository" value="/opt/opennms/share/rrd/response" /> (5)
<parameter key="rrd-base-name" value="dhcp" /> (6)
<parameter key="ds-name" value="dhcp" /> (7)
</service>
<monitor service="DHCP" class-name="org.opennms.netmgt.poller.monitors.DhcpMonitor"/> (8)| 1 | Number of attempts to test a service’s status. |
| 2 | Timeout for the isReachable method, in milliseconds. |
| 3 | Sets the poller’s relay mode. |
| 4 | When extendedMode is false, the DHCP poller sends a DISCOVER. When extendedMode is true, the DHCP poller sends a DISCOVER. |
| 5 | Base directory of an RRD repository in which to store this service monitor’s response-time samples. |
| 6 | The name of the RRD file (minus the .rrd or .jrb file extension). |
| 7 | Name of the RRD data source (DS) in which to store this service monitor’s response-time samples. |
| 8 | Required monitor section. |
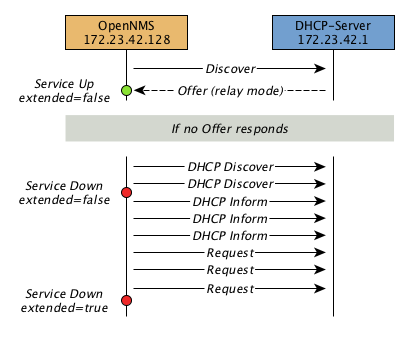
Example: testing DHCP server in a different subnet in extended mode
You can use the same monitor in poller-configuration.xml as in the above example.
<service name="DHCP" interval="300000" user-defined="false" status="on">
<parameter key="retry" value="2" /> (1)
<parameter key="timeout" value="3000" /> (2)
<parameter key="relayMode" value="true"/> (3)
<parameter key="extendedMode" value="false"/> (4)
<parameter key="myIpAddress" value="1.2.3.4"/> (8)
<parameter key="rrd-repository" value="/opt/opennms/share/rrd/response" /> (5)
<parameter key="rrd-base-name" value="dhcp" /> (6)
<parameter key="ds-name" value="dhcp" /> (7)
</service>
<monitor service="DHCP" class-name="org.opennms.netmgt.poller.monitors.DhcpMonitor"/> (9)| 1 | Number of attempts to test a service’s status. |
| 2 | Timeout for the isReachable method, in milliseconds. |
| 3 | Sets the poller’s relay mode. |
| 4 | When extendedMode is false, the DHCP poller sends a DISCOVER. When extendedMode is true, the DHCP poller sends a DISCOVER. |
| 5 | Base directory of an RRD repository in which to store this service monitor’s response-time samples. |
| 6 | The name of the RRD file (minus the .rrd or .jrb file extension). |
| 7 | Name of the RRD data source (DS) in which to store this service monitor’s response-time samples. |
| 8 | If relayMode is set to true, this parameter will usually be set to the IP address of the Meridian server. |
| 9 | Required monitor section. |
If in extendedMode, the time required to complete the poll for an unresponsive node increases by a factor of three.
We recommend that you limit the number of retries to a small number.
|