Thresholding
A threshold lets you define limits against a managed entity’s network performance metrics. When a value goes above or below the specified limit, an event is triggered. The following limit types are supported:
-
High
-
Low
-
Absolute value
-
Relative change
How it works
Meridian uses collectors to collect data for a particular protocol or a family of protocols (SNMP, JMX, HTTP, XML/JSON, WS-Management/WinRM, JDBC). You can configure individual collectors in a collector package—this essentially defines the set of instructions that drives their behavior.
Collectd gathers and stores performance data from collectors. This is the data against which Meridian evaluates thresholds. Thresholds trigger events when specific values are met, and notifications and alarms can be configured for these events.
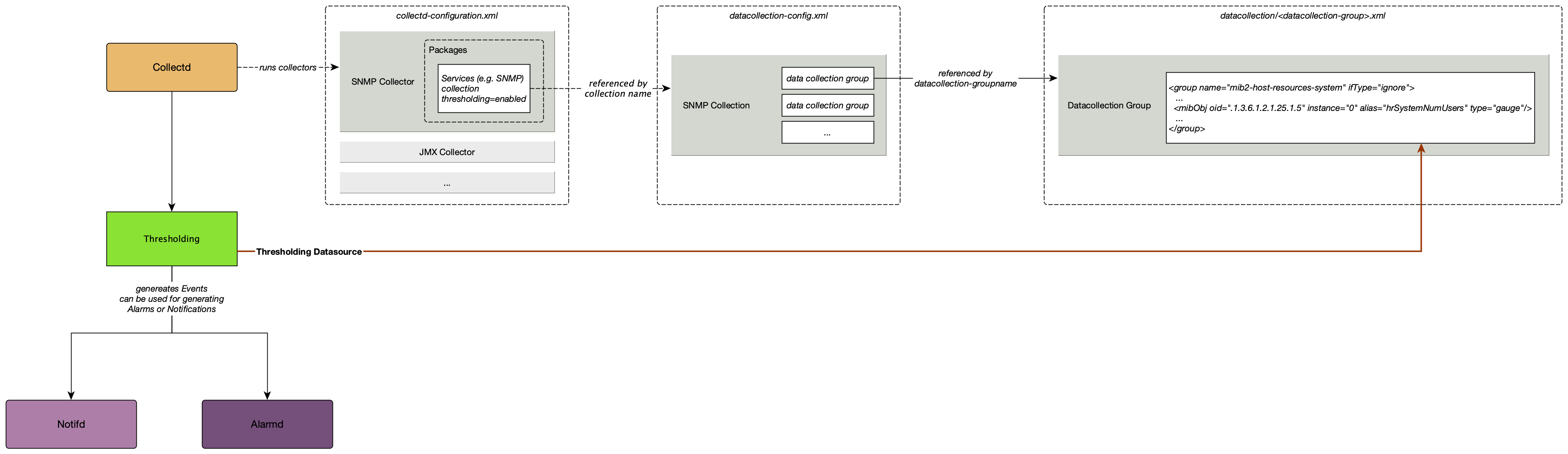
Meridian uses four thresholding algorithms to trigger an event (see Step 5: Set up a Threshold in the Quick Start section for more information). Meridian applies these algorithms against any performance data collected by collectd or pushed to telemetryd. This includes, but is not limited to, metrics such as CPU load, bandwidth, disk space, and so on.
For information on setting and configuring collectors, collectd, and collectd-configuration.xml, see Performance Management.