IFTTT Integration
The IFTTT service lets you combine web applications using simple conditional instructions. Each supported service has several triggers that you can use to trigger the actions of other services. This lets you, for example, change the brightness and color of a smart bulb, and send messages or date information to IoT devices.
The Horizon integration uses the Webhooks service, and lets you trigger actions when it receives a specific web request. It operates as follows: Horizon polls for alarms and matches the alarm reduction key against a given filter, and the alarm’s associated nodes against a given category filter. For the resulting alarm, the maximum severity is set and the total count is computed. If one of these values has changed since the last poll, one or more events specified for the computed maximum severity will be sent to IFTTT.
IFTTT configuration
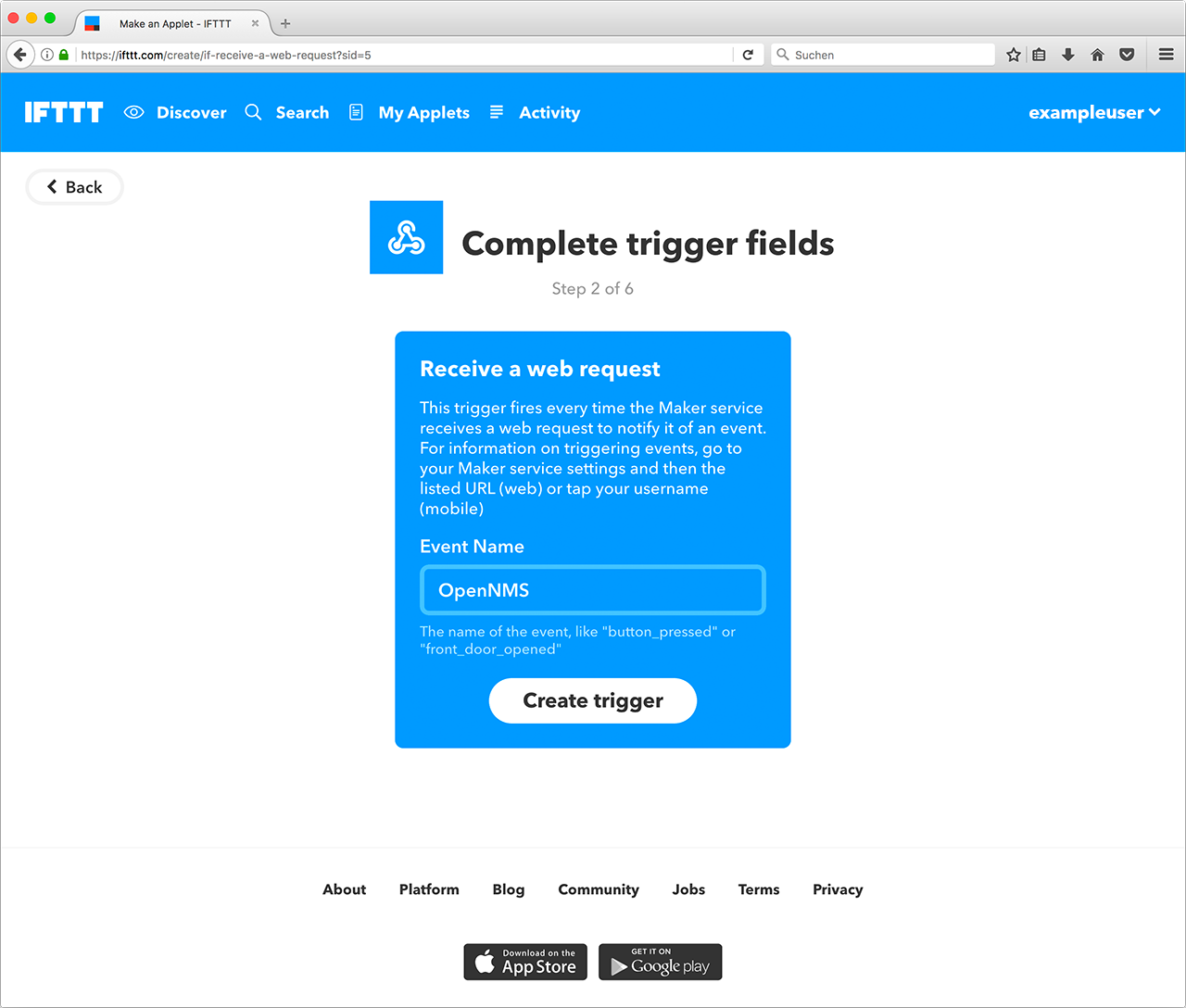
To use the IFTTT integration in Horizon, you must have an IFTTT account. The account lets you create applets that combine a trigger with an action. For example, you can use the Webhooks service as the trigger, and define the event name "OpenNMS". You can combine this trigger with any supported service and its actions.
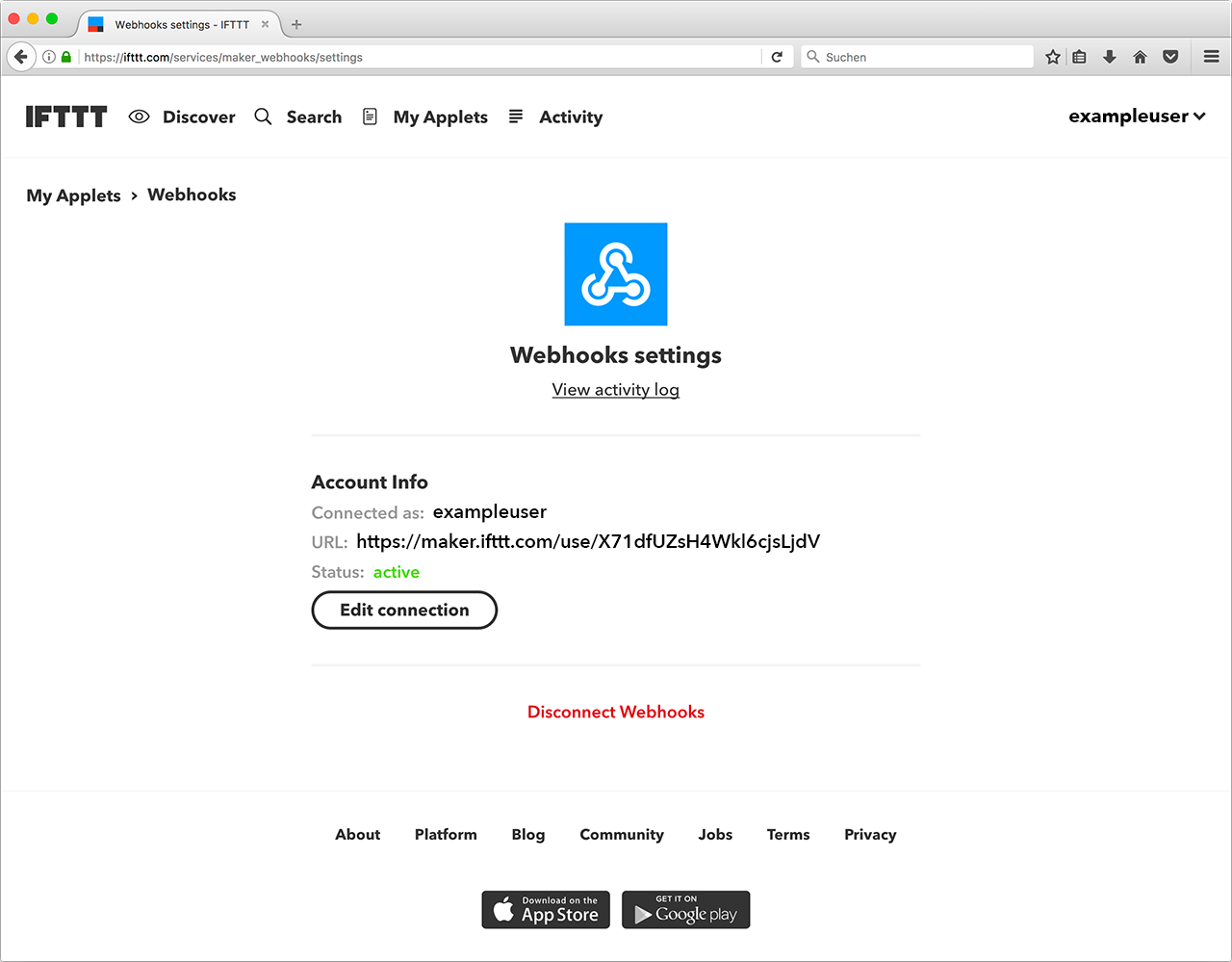
To find your key, navigate to the settings for the Webhooks service and copy the service URL.
In this example, the key is X71dfUZsH4Wkl6cjsLjdV:
In Horizon, you must have a configuration that defines which event names are sent on an alarm count or a severity change.
ifttt-config.xml contains trigger packages.
By default, trigger packages are evaluated as follows:
-
Horizon retrieves all alarms with associated nodes.
-
Each trigger package defines whether to take into account only acknowledged alarms.
-
It computes maximum severity and alarm count for each trigger package’s category filter and reduction key filter.
-
It triggers all events defined in the corresponding trigger sets for the computed maximum severity.
The category and reduction key filters accept Java regular expressions. Using an empty category filter will use all unacknowledged alarms regardless of whether these alarms have nodes assigned.
Each trigger in a set defines the event name to trigger and three additional values. You can use these values to set additional attributes for the corresponding IFTTT applet action.
You can define the following trigger sets:
| Name | Behavior |
|---|---|
ON |
Turn a device on when the IFTTT alarm polling daemon starts. |
OFF |
Turn a device off when the IFTTT alarm polling daemon stops. |
NORMAL |
If severity is NORMAL. |
WARNING |
If severity is WARNING. |
MINOR |
If severity is MINOR. |
MAJOR |
If severity is MAJOR. |
CRITICAL |
If severity is CRITICAL. |
You can use the ON and OFF events when initializing devices or powering them up or down.
Horizon configuration
Enable IFTTT alarm polling by setting enabled to true in ifttt-config.xml.
You can also configure the polling interval.
The trigger package in ifttt-config.xml defines the trigger sets, which themselves define sequences of events to be triggered at IFTTT.
Each trigger defines the eventName and an additional delay.
This lets you defer the next trigger in a set.
Example
The following example shows the configuration file for a Wi-Fi light bulb that is controlled via IFTTT.
The defined applets use value1 to set the color temperature and value2 to set the brightness.
The third value demonstrates how placeholders are used.
For the severity-based trigger sets, you can use the following placeholders in the three value fields:
-
%os%/%oldSeverity: Old severity -
%ns%/%newSeverity%: New severity -
%oc%/%oldCount: Old alarm count -
%nc%/%newCount%: New alarm count
This is useful for sending messages or operating LED displays via IFTTT.
<ifttt-config enabled="true" key="X71dfUZsH4Wkl6cjsLjdV" pollInterval="30">
<trigger-package categoryFilter="Routers|Switches" reductionKeyFilter=".*" onlyUnacknowledged="true">
<trigger-set name="ON">
<trigger eventName="on" delay="0">
<value1></value1>
<value2></value2>
<value3></value3>
</trigger>
</trigger-set>
<trigger-set name="OFF">
<trigger eventName="off" delay="0">
<value1></value1>
<value2></value2>
<value3></value3>
</trigger>
</trigger-set>
<trigger-set name="NORMAL">
<trigger eventName="OpenNMS" delay="0">
<value1>#336600</value1>
<value2>0.40</value2>
<value3>%os%,%ns%,%oc%,%nc%</value3>
</trigger>
</trigger-set>
<trigger-set name="WARNING">
<trigger eventName="OpenNMS" delay="0">
<value1>#FFCC00</value1>
<value2>0.50</value2>
<value3>%os%,%ns%,%oc%,%nc%</value3>
</trigger>
</trigger-set>
<trigger-set name="MINOR">
<trigger eventName="OpenNMS" delay="0">
<value1>#FF9900</value1>
<value2>0.60</value2>
<value3>%os%,%ns%,%oc%,%nc%</value3>
</trigger>
</trigger-set>
<trigger-set name="MAJOR">
<trigger eventName="OpenNMS" delay="0">
<value1>#CC3300</value1>
<value2>0.70</value2>
<value3>%os%,%ns%,%oc%,%nc%</value3>
</trigger>
</trigger-set>
<trigger-set name="CRITICAL">
<trigger eventName="OpenNMS" delay="0">
<value1>#FF0000</value1>
<value2>0.80</value2>
<value3>%os%,%ns%,%oc%,%nc%</value3>
</trigger>
</trigger-set>
<trigger-package>
</ifttt-config>
Metadata expressions can also be used in the key attribute of the ifttt-config.xml configuration file.
This allows the user to also reference an API key stored in the secure credentials vault.
|