Business Service Monitoring
While Meridian detects issues in your network by device, interface or service, the Business Service Monitoring (BSM) takes it one step further. The BSM components let you monitor and model high-level Business Services (BS) and help you quickly identify the most critical problems affecting them. With the BSM feature it is possible to model a high level BS context around the technical Service Monitors provided in Meridian. To indicate which BS is affected by events at the technical Service Monitors level, a BS Operational Status is calculated.
As an example, let’s assume a company runs an online store. Customers log in, select items, place them in the shopping cart and checkout using a payment system. The whole service is provided by a few web servers and access data from databases. To monitor the status of the databases, a SQL service monitor on each database server is configured. For testing the web servers a HTTP service monitor is used for each of them. Covering the overall functionality a Page Sequence Monitor (PSM) is used to test the login, shop and payment workflow through the provided web portal. A possible representation of the whole system hierarchy is shown in figure Example scenario for a web shop.
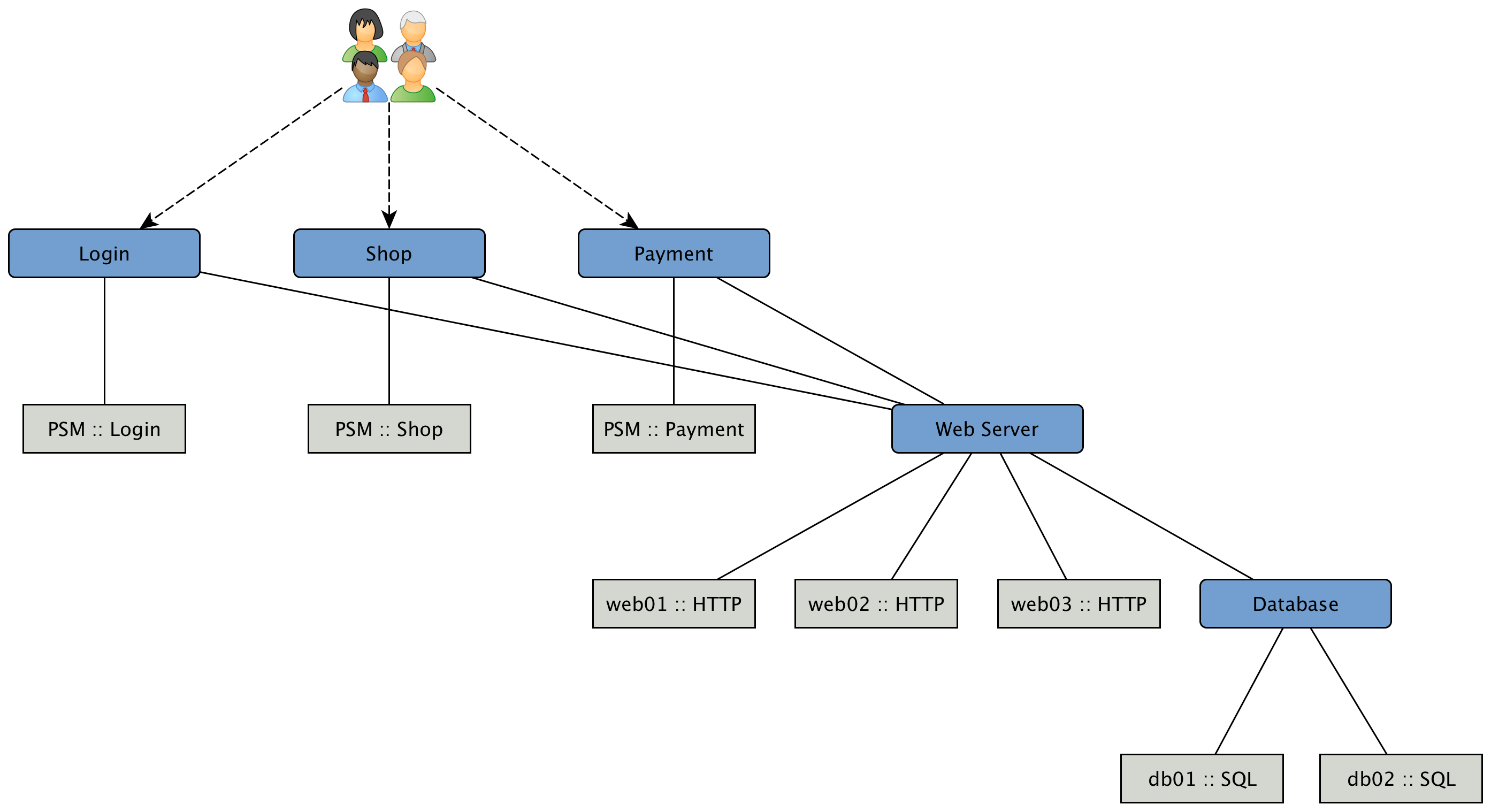
To be able to model this scenarios the BSM functions can be used. The Business Service Monitoring (BSM) feature includes the following components:
-
Business Service Monitoring Daemon (BSMD): Maintains and drives the state of all BS
-
Business Service Editor: Web application that lets you create, update, or delete BS
-
Topology View for Business Services: Visual representation of the Business Service Hierarchy as a component of the Topology User Interface.
-
BSM ReST API: ReST based API to create, read, update or delete BS