Link Layer Discovery
The Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is a vendor-neutral link layer protocol. Network devices use it to advertise their identity, capabilities, and neighbors.
LLDP performs functions similar to several proprietary protocols, such as the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), Extreme Discovery Protocol (EDP), Foundry Discovery Protocol (FDP), Nortel Discovery Protocol (also known as SONMP), and Microsoft’s Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP).
Only nodes with a running LLDP process can be part of the link discovery.
The data is similar to running the show lldp neighbor command on a device’s command line.
Linux and Windows servers don’t have an LLDP process running by default, and will not be part of the link discovery unless an LLDP agent is manually installed and configured.
|
You can find generic information about the LLDP process in the LLDP Information box on any device’s Node Detail page.
LLDP Topology Updater
The LLDP Topology Updater consolidates LLDP data and provides the LLDP OnmsTopology. Only full bidirectional connections between two LLDP-supported devices become edges in the topology. For example, Node A and Node B are connected by an edge if, and only if, there is an LLDP MIB port connection in Node A to Node B, and vice versa.
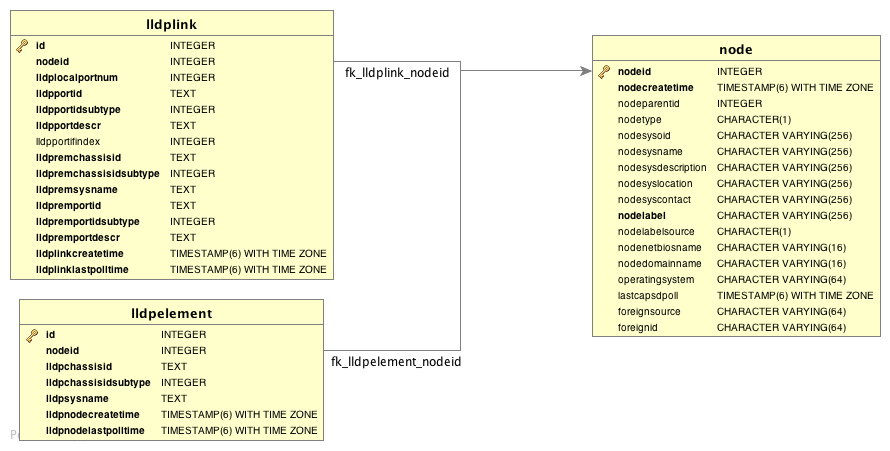
Information gathered from supported OIDs is stored in the following database tables:
Supported OIDs
The following OIDs are supported for the discovery and construction of the LLDP network topology. The LLDP Discovery Collector collects them:
| Name | Description | OID |
|---|---|---|
lldpLocChassisIdSubtype |
Type of encoding used to identify the chassis associated with the local system ( |
.1.0.8802.1.1.2.1.3.1.0 |
lldpLocChassisId |
String value used to identify the chassis component associated with the local system. |
.1.0.8802.1.1.2.1.3.2.0 |
lldpLocSysName |
String value used to identify the system name of the local system.
If the local agent supports IETF RFC 3418, |
.1.0.8802.1.1.2.1.3.3.0 |
lldpLocPortIdSubtype |
Type of port identifier encoding used in the associated |
.1.0.8802.1.1.2.1.3.7.1.2 |
lldpLocPortId |
String value used to identify the port component associated with a given port in the local system. |
.1.0.8802.1.1.2.1.3.7.1.3 |
lldpLocPortDesc |
String value used to identify the 802 LAN station’s port description that is associated with the local system.
If the local agent supports IETF RFC 2863, |
.1.0.8802.1.1.2.1.3.7.1.4 |
lldpRemChassisIdSubtype |
Type of encoding used to identify the chassis associated with the local system ( |
.1.0.8802.1.1.2.1.4.1.1.4 |
lldpRemChassisId |
String value used to identify the chassis component associated with the remote system. |
.1.0.8802.1.1.2.1.4.1.1.5 |
lldpRemPortIdSubtype |
Type of port identifier encoding used in the associated |
.1.0.8802.1.1.2.1.4.1.1.6 |
lldpRemPortId |
String value used to identify the port component that is associated with the remote system. |
.1.0.8802.1.1.2.1.4.1.1.7 |
lldpRemPortDesc |
String value used to identify the description of the given port that is associated with the remote system. |
.1.0.8802.1.1.2.1.4.1.1.8 |
lldpRemSysName |
String value used to identify the remote system’s name. |
.1.0.8802.1.1.2.1.4.1.1.9 |