Expressions
HELM supports JEXL mathematical and conditional operators in performance data queries. Use them to combine or otherwise transform one or more series into a new series. For example, you could specify a filter to display the SUM of data from different attribute queries (such as available memory on two nodes).
This section provides sample expressions to illustrate how to use them. For additional documentation on expressions, see the following:
-
Measurements API documentation of your OpenNMS version
Create an expression
Before creating an expression, you need to define one or more attribute queries on a performance datasource. You can then use the attribute name or the series label (attribute alias) as part of the expression you create.
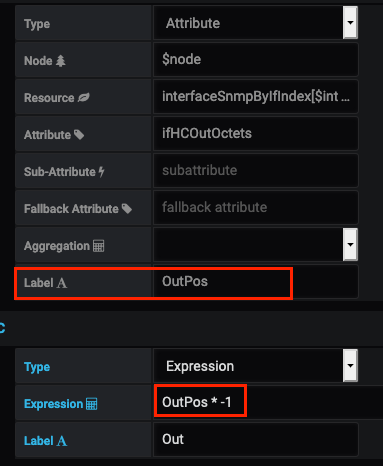
The following queries on the total number of octets transmitted out of an interface, with an expression to change the value to a negative number.
Since traffic in and out values might be similar, and therefore overlap on a graph, setting the "out" value to a negative number will avoid this overlap, making the graph easier to read.
Note that the expression uses the "OutPos" series label as the alias for IfHCOutOctets:
Value in bits
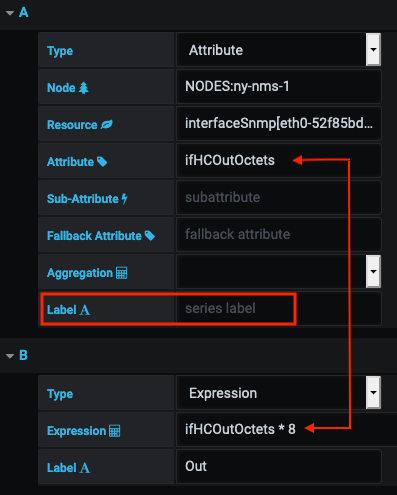
The ifHCOutOctets value is in bytes, but you want to display it in bits.
Create a simple expression to multiply the data by 8: ifHCOutOctets * 8.
Note that in this case, there is no series label, so the expression uses the IfHCOutOctets name:
Add several series together
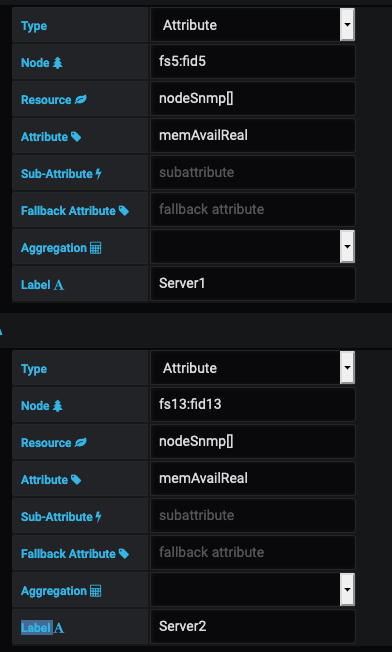
You are running a distributed cache across multiple servers. You want to determine the amount of memory available across all of the servers.
First, create attribute queries on memAvailReal (the amount of real/physical memory currently unused or available) for each server:
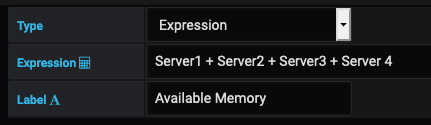
Then create an expression query that adds each series together:
Server1 + Server2 + Server3 + Server4
Add a series with null value expression
In situations where a value returned in a series is not a number (NA), using a null value will ensure your expression returns a number.
For example, if you are adding Series A plus Series B, and Series B is NA, but Series A is a number (for example, "5"), then it becomes 5+NA, which equals NA.
An expression that treats NA as a null value means the result would be 5+0, which provides a numeric answer, as in the following expression:
(A == null ? 0 : A) + (B == null ? 0 : B)
In fact, JEXL has an abbreviation for non-null, non-false ternary:
(A ?: 0) + (B ?: 0)